LeetCode —— dfs和bfs
最佳答案 问答题库608位专家为你答疑解惑
797. 所有可能的路径
给你一个有 n 个节点的 有向无环图(DAG),请你找出所有从节点 0 到节点 n-1 的路径并输出(不要求按特定顺序)。 graph[i] 是一个从节点 i 可以访问的所有节点的列表(即从节点 i 到节点 graph[i][j]存在一条有向边)。
示例1:输入:graph = [[1,2],[3],[3],[]] 输出:[[0,1,3],[0,2,3]]
示例2:输入:graph = [[4,3,1],[3,2,4],[3],[4],[]] 输出:[[0,4],[0,3,4],[0,1,3,4],[0,1,2,3,4],[0,1,4]]
// dfs
class Solution {List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();public List<List<Integer>> allPathsSourceTarget(int[][] graph) {path.add(0);dfs(graph, 0);return list;}public void dfs(int[][] graph, int node){if(node == graph.length - 1){list.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}for(int i = 0; i < graph[node].length; i++){path.add(graph[node][i]);dfs(graph, graph[node][i]);path.removeLast();}}
}200. 岛屿数量
给你一个由 '1'(陆地)和 '0'(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
示例1:
输入:grid = [["1","1","1","1","0"],["1","1","0","1","0"],["1","1","0","0","0"],["0","0","0","0","0"] ] 输出:1
// dfs
class Solution {public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {int count = 0;for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++){for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++){if(grid[i][j] == '1'){count++;dfs(grid, i, j);}}}return count;}public void dfs(char[][] grid, int i, int j){if(i < 0 || i >= grid.length || j < 0 || j >= grid[0].length || grid[i][j] == '0'){return;}grid[i][j] = '0';dfs(grid, i - 1, j);dfs(grid, i + 1, j);dfs(grid, i, j - 1);dfs(grid, i, j + 1);}
}// bfs
class Solution {public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {int count = 0;for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++){for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++){if(grid[i][j] == '1'){count++;bfs(grid, i, j);}}}return count;}public void bfs(char[][] grid, int i, int j){Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});while(!queue.isEmpty()){int[] cur = queue.poll();i = cur[0];j = cur[1];if(i >= 0 && i < grid.length && j >= 0 && j < grid[0].length && grid[i][j] == '1'){grid[i][j] = '0';queue.offer(new int[]{i - 1, j});queue.offer(new int[]{i + 1, j});queue.offer(new int[]{i, j - 1});queue.offer(new int[]{i, j + 1});}}}
}695. 岛屿的最大面积
给你一个大小为 m x n 的二进制矩阵 grid 。岛屿 是由一些相邻的 1 (代表土地) 构成的组合,这里的「相邻」要求两个 1 必须在 水平或者竖直的四个方向上 相邻。你可以假设 grid 的四个边缘都被 0(代表水)包围着。岛屿的面积是岛上值为 1 的单元格的数目。计算并返回 grid 中最大的岛屿面积。如果没有岛屿,则返回面积为 0 。

输入:grid = [[0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],[0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0]] 输出:6
// dfs
class Solution {int area;public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {int maxArea = 0;for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++){for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++){if(grid[i][j] == 1){area = 0;dfs(grid, i, j);maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, area);}}}return maxArea;}public void dfs(int[][] grid, int i, int j){if(i < 0 || i >= grid.length || j < 0 || j >= grid[0].length || grid[i][j] == 0){return;}area++;grid[i][j] = 0;dfs(grid, i - 1, j);dfs(grid, i + 1, j);dfs(grid, i, j - 1);dfs(grid, i, j + 1);}
}// bfs
class Solution {int area;public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {int maxArea = 0;for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++){for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++){if(grid[i][j] == 1){area = 0;bfs(grid, i, j);maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, area);}}}return maxArea;}public void bfs(int[][] grid, int i, int j){Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});while(!queue.isEmpty()){int[] cur = queue.poll();i = cur[0];j = cur[1];if(i >= 0 && i < grid.length && j >= 0 && j < grid[0].length && grid[i][j] == 1){area++;grid[i][j] = 0;queue.offer(new int[]{i - 1, j});queue.offer(new int[]{i + 1, j});queue.offer(new int[]{i, j - 1});queue.offer(new int[]{i, j + 1});}}}
}695. 岛屿的周长
给定一个 row x col 的二维网格地图 grid ,其中:grid[i][j] = 1 表示陆地, grid[i][j] = 0 表示水域。网格中的格子 水平和垂直 方向相连(对角线方向不相连)。整个网格被水完全包围,但其中恰好有一个岛屿(或者说,一个或多个表示陆地的格子相连组成的岛屿)。岛屿中没有“湖”(“湖” 指水域在岛屿内部且不和岛屿周围的水相连)。格子是边长为 1 的正方形。网格为长方形,且宽度和高度均不超过 100 。计算这个岛屿的周长。
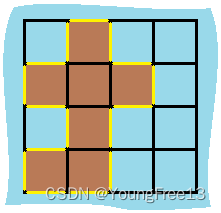
示例:输入:grid = [[0,1,0,0],[1,1,1,0],[0,1,0,0],[1,1,0,0]] 输出:16
// dfs
class Solution {int count = 0;public int islandPerimeter(int[][] grid) {for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++){for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++){if(grid[i][j] == 1){dfs(grid, i, j);}}}return count;}public void dfs(int[][] grid, int i, int j){if(i < 0 || i >= grid.length || j < 0 || j >= grid[0].length || grid[i][j] == 0){count++;return;}if(grid[i][j] == 2){return;}grid[i][j] = 2;dfs(grid, i - 1, j);dfs(grid, i + 1, j);dfs(grid, i, j - 1);dfs(grid, i, j + 1);}
}827. 最大人工岛屿
给你一个大小为 n x n 二进制矩阵 grid 。最多 只能将一格 0 变成 1 。返回执行此操作后,grid 中最大的岛屿面积是多少?岛屿 由一组上、下、左、右四个方向相连的 1 形成。
示例:输入: grid = [[1, 0], [0, 1]] 输出: 3
// dfs
class Solution {int islandSize; // 每个岛屿的大小public int largestIsland(int[][] grid) {int[][] positions = new int[][]{{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}};int m = grid.length;int n = grid[0].length;Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); // key为岛屿编号,value为岛屿大小int islandNumber = 2; // 岛屿编号从2开始,与0和1进行区分for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){if(grid[i][j] == 1){islandSize = 0;dfs(grid, i, j, islandNumber);map.put(islandNumber, islandSize);islandNumber++;}}}int result = Integer.MIN_VALUE;for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){if(grid[i][j] != 0){continue;}int curSize = 1;Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();for(int[] pos : positions){int newRow = i + pos[0];int newColumn = j + pos[1];if(newRow < 0 || newRow >= m || newColumn < 0 || newColumn >= n || grid[newRow][newColumn] == 0){continue;}islandNumber = grid[newRow][newColumn];if(set.contains(islandNumber) || !map.containsKey(islandNumber)){continue;}set.add(islandNumber);curSize += map.get(islandNumber);}result = Math.max(result, curSize);}}return result == Integer.MIN_VALUE ? m * n : result;}public void dfs(int[][] grid, int i, int j, int islandNumber){if(i < 0 || i >= grid.length || j < 0 || j >= grid[0].length || grid[i][j] != 1){return;}islandSize++;grid[i][j] = islandNumber;dfs(grid, i - 1, j, islandNumber);dfs(grid, i + 1, j, islandNumber);dfs(grid, i, j - 1, islandNumber);dfs(grid, i, j + 1, islandNumber);}
}1020. 飞地的数量
给你一个大小为 m x n 的二进制矩阵 grid ,其中 0 表示一个海洋单元格、1 表示一个陆地单元格。一次 移动 是指从一个陆地单元格走到另一个相邻(上、下、左、右)的陆地单元格或跨过 grid 的边界。返回网格中 无法 在任意次数的移动中离开网格边界的陆地单元格的数量。

示例:输入:grid = [[0,0,0,0],[1,0,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[0,0,0,0]] 输出:3
// dfs
class Solution {public int numEnclaves(int[][] grid) {for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++){ if(grid[i][0] == 1){ // 左侧dfs(grid, i, 0);}if(grid[i][grid[0].length - 1] == 1){ // 右侧dfs(grid, i, grid[0].length - 1);}}for(int j = 1; j < grid[0].length - 1; j++){ if(grid[0][j] == 1){ // 上侧dfs(grid, 0, j);}if(grid[grid.length - 1][j] == 1){ // 下侧dfs(grid, grid.length - 1, j);}}int count = 0;for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++){for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++){if(grid[i][j] == 1){count++;}}}return count;}public void dfs(int[][] grid, int i, int j){if(i < 0 || i >= grid.length || j < 0 || j >= grid[0].length || grid[i][j] == 0){return;}grid[i][j] = 0;dfs(grid, i - 1, j);dfs(grid, i + 1, j);dfs(grid, i, j - 1);dfs(grid, i, j + 1);}
}// bfs
class Solution {public int numEnclaves(int[][] grid) {for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++){if(grid[i][0] == 1){ // 左侧bfs(grid, i, 0);}if(grid[i][grid[0].length - 1] == 1){ // 右侧bfs(grid, i, grid[0].length - 1);}}for(int j = 1; j < grid[0].length - 1; j++){if(grid[0][j] == 1){ // 上侧bfs(grid, 0, j);}if(grid[grid.length - 1][j] == 1){ // 下侧bfs(grid, grid.length - 1, j);}}int count = 0;for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++){for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++){if(grid[i][j] == 1){count++;}}}return count;}public void bfs(int[][] grid, int i, int j){Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});while(!queue.isEmpty()){int[] cur = queue.poll();i = cur[0];j = cur[1];if(i >= 0 && i < grid.length && j >= 0 && j < grid[0].length && grid[i][j] == 1){grid[i][j] = 0;queue.offer(new int[]{i - 1, j});queue.offer(new int[]{i + 1, j});queue.offer(new int[]{i, j - 1});queue.offer(new int[]{i, j + 1});}}}
}130. 被围绕的区域
给你一个 m x n 的矩阵 board ,由若干字符 'X' 和 'O' ,找到所有被 'X' 围绕的区域,并将这些区域里所有的 'O' 用 'X' 填充。

// dfs
class Solution {public void solve(char[][] board) {for(int i = 0; i < board.length; i++){if(board[i][0] == 'O'){dfs(board, i, 0);}if(board[i][board[0].length - 1] == 'O'){dfs(board, i, board[0].length - 1);}}for(int j = 1; j < board[0].length - 1; j++){if(board[0][j] == 'O'){dfs(board, 0, j);}if(board[board.length - 1][j] == 'O'){dfs(board, board.length - 1, j);}}for(int i = 0; i < board.length; i++){for(int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++){if(board[i][j] == 'A'){board[i][j] = 'O';}else if(board[i][j] == 'O'){board[i][j] = 'X';}}}}public void dfs(char[][] board, int i, int j){if(i < 0 || i >= board.length || j < 0 || j >= board[0].length || board[i][j] == 'X' || board[i][j] == 'A'){return;}board[i][j] = 'A';dfs(board, i - 1, j);dfs(board, i + 1, j);dfs(board, i, j - 1);dfs(board, i, j + 1);}
}// bfs
class Solution {public void solve(char[][] board) {for(int i = 0; i < board.length; i++){if(board[i][0] == 'O'){bfs(board, i, 0);}if(board[i][board[0].length - 1] == 'O'){bfs(board, i, board[0].length - 1);}}for(int j = 1; j < board[0].length - 1; j++){if(board[0][j] == 'O'){bfs(board, 0, j);}if(board[board.length - 1][j] == 'O'){bfs(board, board.length - 1, j);}}for(int i = 0; i < board.length; i++){for(int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++){if(board[i][j] == 'A'){board[i][j] = 'O';}else if(board[i][j] == 'O'){board[i][j] = 'X';}}}}public void bfs(char[][] board, int i, int j){Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});while(!queue.isEmpty()){int[] cur = queue.poll();i = cur[0];j = cur[1];if(i >= 0 && i < board.length && j >= 0 && j < board[0].length && board[i][j] == 'O'){board[i][j] = 'A';queue.offer(new int[]{i - 1, j});queue.offer(new int[]{i + 1, j});queue.offer(new int[]{i, j - 1});queue.offer(new int[]{i, j + 1});}}}
}417. 太平洋大西洋水流问题
有一个 m × n 的矩形岛屿,与 太平洋 和 大西洋 相邻。 “太平洋” 处于大陆的左边界和上边界,而 “大西洋” 处于大陆的右边界和下边界。这个岛被分割成一个由若干方形单元格组成的网格。给定一个 m x n 的整数矩阵 heights , heights[r][c] 表示坐标 (r, c) 上单元格 高于海平面的高度 。岛上雨水较多,如果相邻单元格的高度 小于或等于 当前单元格的高度,雨水可以直接向北、南、东、西流向相邻单元格。水可以从海洋附近的任何单元格流入海洋。返回网格标 result 的 2D 列表 ,其中 result[i] = [ri, ci] 表示雨水从单元格 (ri, ci) 流动 既可流向太平洋也可流向大西洋 。

// dfs
class Solution {int[][] positions = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}};public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {int m = heights.length;int n = heights[0].length;boolean[][] pacific = new boolean[m][n];boolean[][] atlantic = new boolean[m][n];for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){dfs(heights, i, 0, pacific);dfs(heights, i, n - 1, atlantic);}for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){dfs(heights, 0, j, pacific);dfs(heights, m - 1, j, atlantic);}List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){if(pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]){List<Integer> item = new ArrayList<>();item.add(i);item.add(j);list.add(item);}}}return list;}public void dfs(int[][] heights, int i, int j, boolean[][] ocean){if(ocean[i][j]){return;}ocean[i][j] = true;for(int[] pos : positions){int newRow = i + pos[0];int newColumn = j + pos[1];if(newRow >= 0 && newRow < heights.length && newColumn >= 0 && newColumn < heights[0].length && heights[i][j] <= heights[newRow][newColumn]){dfs(heights, newRow, newColumn, ocean);}}}
}// bfs
class Solution {int[][] positions = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}};public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {int m = heights.length;int n = heights[0].length;boolean[][] pacific = new boolean[m][n];boolean[][] atlantic = new boolean[m][n];for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){bfs(heights, i, 0, pacific);bfs(heights, i, n - 1, atlantic);}for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){bfs(heights, 0, j, pacific);bfs(heights, m - 1, j, atlantic);}List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){if(pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]){List<Integer> item = new ArrayList<>();item.add(i);item.add(j);list.add(item);}}}return list;}public void bfs(int[][] heights, int i, int j, boolean[][] ocean){ocean[i][j] = true;Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});while(!queue.isEmpty()){int[] cur = queue.poll();for(int[] pos : positions){int newRow = cur[0] + pos[0];int newColumn = cur[1] + pos[1];if(newRow >= 0 && newRow < heights.length && newColumn >= 0 && newColumn < heights[0].length && heights[cur[0]][cur[1]] <= heights[newRow][newColumn] && !ocean[newRow][newColumn]){ocean[newRow][newColumn] = true;queue.offer(new int[]{newRow, newColumn});}}}}
}841. 钥匙和房间
有 n 个房间,房间按从 0 到 n - 1 编号。最初,除 0 号房间外的其余所有房间都被锁住。你的目标是进入所有的房间。然而,你不能在没有获得钥匙的时候进入锁住的房间。当你进入一个房间,你可能会在里面找到一套不同的钥匙,每把钥匙上都有对应的房间号,即表示钥匙可以打开的房间。你可以拿上所有钥匙去解锁其他房间。给你一个数组 rooms 其中 rooms[i] 是你进入 i 号房间可以获得的钥匙集合。如果能进入 所有 房间返回 true,否则返回 false。
示例1:输入:rooms = [[1],[2],[3],[]] 输出:true
示例2:输入:rooms = [[1,3],[3,0,1],[2],[0]] 输出:false
// dfs
class Solution {public boolean canVisitAllRooms(List<List<Integer>> rooms) {boolean[] visited = new boolean[rooms.size()];dfs(rooms, visited, 0);for(int i = 0; i < visited.length; i++){if(!visited[i]){return false;}}return true;}public void dfs(List<List<Integer>> rooms, boolean[] visited, int key){if(visited[key]){return;}visited[key] = true;List<Integer> curRoom = rooms.get(key);for(int i = 0; i < curRoom.size(); i++){dfs(rooms, visited, curRoom.get(i));}}
}// bfs
class Solution {public boolean canVisitAllRooms(List<List<Integer>> rooms) {boolean[] visited = new boolean[rooms.size()];bfs(rooms, visited);for(int i = 0; i < visited.length; i++){if(!visited[i]){return false;}}return true;}public void bfs(List<List<Integer>> rooms, boolean[] visited){Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(0);while(!queue.isEmpty()){int curKey = queue.poll();visited[curKey] = true;List<Integer> curRoom = rooms.get(curKey);for(int i = 0; i < curRoom.size(); i++){if(visited[curRoom.get(i)]){continue;}queue.offer(curRoom.get(i));}}}
}99%的人还看了
相似问题
猜你感兴趣
版权申明
本文"LeetCode —— dfs和bfs":http://eshow365.cn/6-21733-0.html 内容来自互联网,请自行判断内容的正确性。如有侵权请联系我们,立即删除!
- 上一篇: WebView 以及如何测试
- 下一篇: react绑定样式实现切换主题改变组件样式