【数据结构】栈详解
最佳答案 问答题库878位专家为你答疑解惑
目录
- 1. 前言
- 2. 栈
- 2.1 栈的概念及结构
- 2.2 如何实现栈
- 2.3 数组栈实现
- 2.3.1 top怎么确定
- 2.3.2 栈顶插入
- 2.3.2.1 栈顶插入分析
- 2.3.2.2 栈顶插入代码实现
- 2.3.3 栈顶删除
- 2.3.4 判空
- 2.3.4.1 分析
- 2.3.4.2 代码实现
- 2.3.5 栈的元素个数
- 2.3.6 栈销毁
- 2.3.7 栈访问数据
- 3. 源代码
- 3.1 Stack.h
- 3.2 Stack.c
- 3.3 test.c
1. 前言
在前面我们一起了解的数据结构有顺序表和链表,这次来介绍栈。
与顺序表和链表相同的是,栈也是常见的数据结构。而与前面两种不同的是,它在农村种的存储,接下来让我们一起来学习一下。
2. 栈
2.1 栈的概念及结构
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。

2.2 如何实现栈

那该如何实现栈呢?
第一种使用数组栈
第二种使用链式栈
链表实现又分为双向链表,和单链表。
双向链表实现,栈顶可以是尾,也可以是头。
单链表实现,栈顶只能是头。

如果只选择一种来实现,那必然是数组,虽然有扩容,但不是频繁扩容。还有另外一个优势,它访问数据,CPU高速缓存命中率比较高,访问第一个,后面都在缓存了。
2.3 数组栈实现
2.3.1 top怎么确定
我们需要考虑top怎么确定?
如果top给0,那么表示的是栈顶还是栈顶位置的下一个?

如果空的时候top给的是0,那么插入一个数据之后top也是0,因为top指向栈顶。
此时就出现了歧义。top==0是一个元素还是空?区分不开。
那该怎么区分呢?
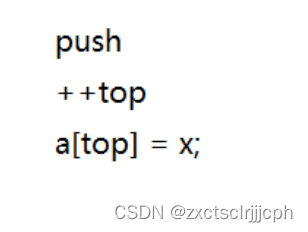
第一种如果top指向栈顶元素,那么top初始时给-1。

这种插入数据时:
要先加加top,再在这个位置赋值。
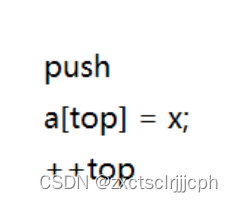
第二种指向栈顶元素的下一个。
此时top初始时就为0。

这种插入数据时:
要先在这个位置赋值,再加加top。
这里插入就取决于怎么初始化栈。
选择第二种来实现代码,这种更简单。
void STInit(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);pst->a = NULL;pst->capacity = 0;pst->top = 0;//第二种
}
2.3.2 栈顶插入
2.3.2.1 栈顶插入分析
插入的代码非常简单:
pst->a[pst->top] = x;pst->top++;
但是在插入之前,要先判断一下栈有没有满,满的化要进行扩容。
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
但我们要初始时候有没有给空间,如果有直接扩两倍,没有就给初始值4。
使用一个三目表达式
int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
如果没有开空间,就直接返回或者结束程序。
if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}
2.3.2.2 栈顶插入代码实现
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{assert(pst);if (pst->top == pst->capacity){int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}pst->a = tmp;pst->capacity = newcapacity;}pst->a[pst->top] = x;pst->top++;
}
2.3.3 栈顶删除
删除很简单,直接top–,就行,但减减之前判断一下top是不是0,加一个断言就行。
代码实现:
void STPop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);// 不为空assert(pst->top > 0);pst->top--;
}
返回栈顶数据的代码:
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);// 不为空assert(pst->top > 0);return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
2.3.4 判空
2.3.4.1 分析
判空这里得看刚开始时:初始时top为0,就要判断top==0。初始为-1,那么就要判断top==-1。
可以用if来判断:
if (pst->top == 0){return true;}else{return false;}
但是有个更简单的:bool类型返回就是真假,利用返回值当结果就行,直接返回pst->top == 0。
2.3.4.2 代码实现
代码实现:
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);/*if (pst->top == 0){return true;}else{return false;}*/return pst->top == 0;
}
2.3.5 栈的元素个数
如果top是指向栈顶元素的下一个,那么元素个数就是top。
如果top就是指向栈顶,那么元素个数就是top+1。

代码实现:
int STSize(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top;
}
2.3.6 栈销毁
直接将元素都free掉,再把它们都置为空。把栈顶和栈空间都置为0。
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);free(pst->a);pst->a = NULL;pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}
2.3.7 栈访问数据
因为栈是后进先出,所以栈不能随便打印。
那怎么打印呢?
判断栈是否为空,然后从栈顶开始访问。
访问了栈顶元素,要想访问下一个就要先将栈顶元素弹出,直到栈为空,就结束。
代码实现:
while (!STEmpty(&s)){printf("%d ", STTop(&s));STPop(&s);}printf("\n");
3. 源代码
3.1 Stack.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>typedef int STDataType;typedef struct Stack
{int* a;int top; // 标识栈顶位置的int capacity;
}ST;void STInit(ST* pst);
void STDestroy(ST* pst);// 栈顶插入删除
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* pst);
STDataType STTop(ST* pst);bool STEmpty(ST* pst);
int STSize(ST* pst);3.2 Stack.c
#include"Stack.h"void STInit(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);pst->a = NULL;pst->capacity = 0;// 表示top指向栈顶元素的下一个位置pst->top = 0;// 表示top指向栈顶元素//pst->top = -1;
}void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);free(pst->a);pst->a = NULL;pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}// 栈顶插入删除
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{assert(pst);if (pst->top == pst->capacity){int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}pst->a = tmp;pst->capacity = newcapacity;}pst->a[pst->top] = x;pst->top++;
}void STPop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);// 不为空assert(pst->top > 0);pst->top--;
}STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);// 不为空assert(pst->top > 0);return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);/*if (pst->top == 0){return true;}else{return false;}*/return pst->top == 0;
}int STSize(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top;
}
3.3 test.c
#include"Stack.h"int main()
{ST s;STInit(&s);STPush(&s, 1);STPush(&s, 2);STPush(&s, 3);printf("%d ", STTop(&s));STPop(&s);printf("%d ", STTop(&s));STPop(&s);STPush(&s, 4);STPush(&s, 5);// 一 对 多// 入栈顺序 -- 出栈顺序while (!STEmpty(&s)){printf("%d ", STTop(&s));STPop(&s);}printf("\n");return 0;
}99%的人还看了
猜你感兴趣
版权申明
本文"【数据结构】栈详解":http://eshow365.cn/6-41664-0.html 内容来自互联网,请自行判断内容的正确性。如有侵权请联系我们,立即删除!
- 上一篇: SpringBoot实现SSE构建实时数据单向推送
- 下一篇: ChatGPT API 学习