【继承之extends关键字和super关键字】
最佳答案 问答题库468位专家为你答疑解惑
文章目录
- 继承是什么?为什么要继承?
- 怎么继承?
- 继承的语法 关键字extends
- 子类中访问父类的成员变量
- 1.子类和父类的成员变量不同名
- 2.子类和父类成员变量同名
- 子类中访问父类的成员方法
- 1. .子类和父类的成员方法名字不同
- 2..子类和父类的成员方法名字相同
- super关键字(在子类中访问父类成员)
- 1. 访问父类的成员方法
- 2.访问父类的成员变量
- 总结
继承是什么?为什么要继承?
有时候创建一些类的成员变量和方法时,会发现它们之间有共同的地方,为了金少重复的代码,提高效率,java的面向对象提出了继承,就是把共同的代码拿出来放进一个类里面,需要调用它的时候继承它就可以了。
总结:继承是一种思想,对共性进行抽取,达到代码复用的效果
怎么继承?
继承的语法 关键字extends
在Java中如果要表示类之间的继承关系,需要借助extends关键字
修饰符 class 子类 extends 父类 {
}
继承前:
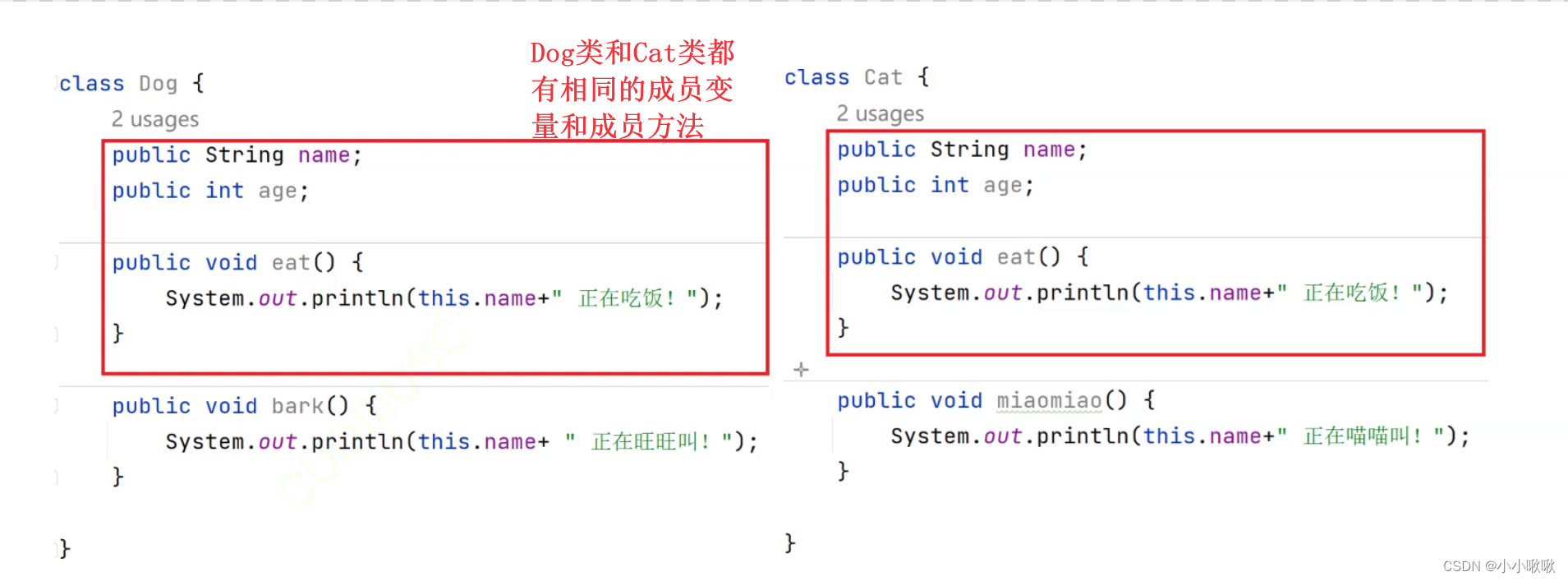
class Cat {public String name;public int age;public void eat() {System.out.println(this.name + "正在吃饭");}public void miao(){System.out.println(this.name+"正在喵喵叫");}
}class Dog{public String name;public int age;public void eat(){System.out.println(this.name+"正在吃饭");}public void bark(){System.out.println(this.name+"正在汪汪叫");}}
继承后:
class Animal{public String name;public int age;public void eat() {System.out.println(this.name + "正在吃饭");}
}
class Cat extends Animal {public void miao(){System.out.println(this.name+"正在喵喵叫");}
}class Dog extends Animal{public void bark(){System.out.println(this.name+"正在汪汪叫");}
}
总结:
Dog和Cat都继承了Animal类,其中:Animal类称为父类/基类或超类,Dog和Cat可以称为Animal的子类/派生类,继承之后,子类可以复用父类中成员
子类中访问父类的成员变量
第一种:
1.子类和父类的成员变量不同名
第二种:
2.子类和父类成员变量同名
在子类方法中 或者 通过子类对象访问成员时:
1.当子类与父类的成员变量同名时,优先使用子类自己的
2.如果访问的成员变量 子类没有 就去访问父类的
3.如果子类和父类都没有,则编译会报错
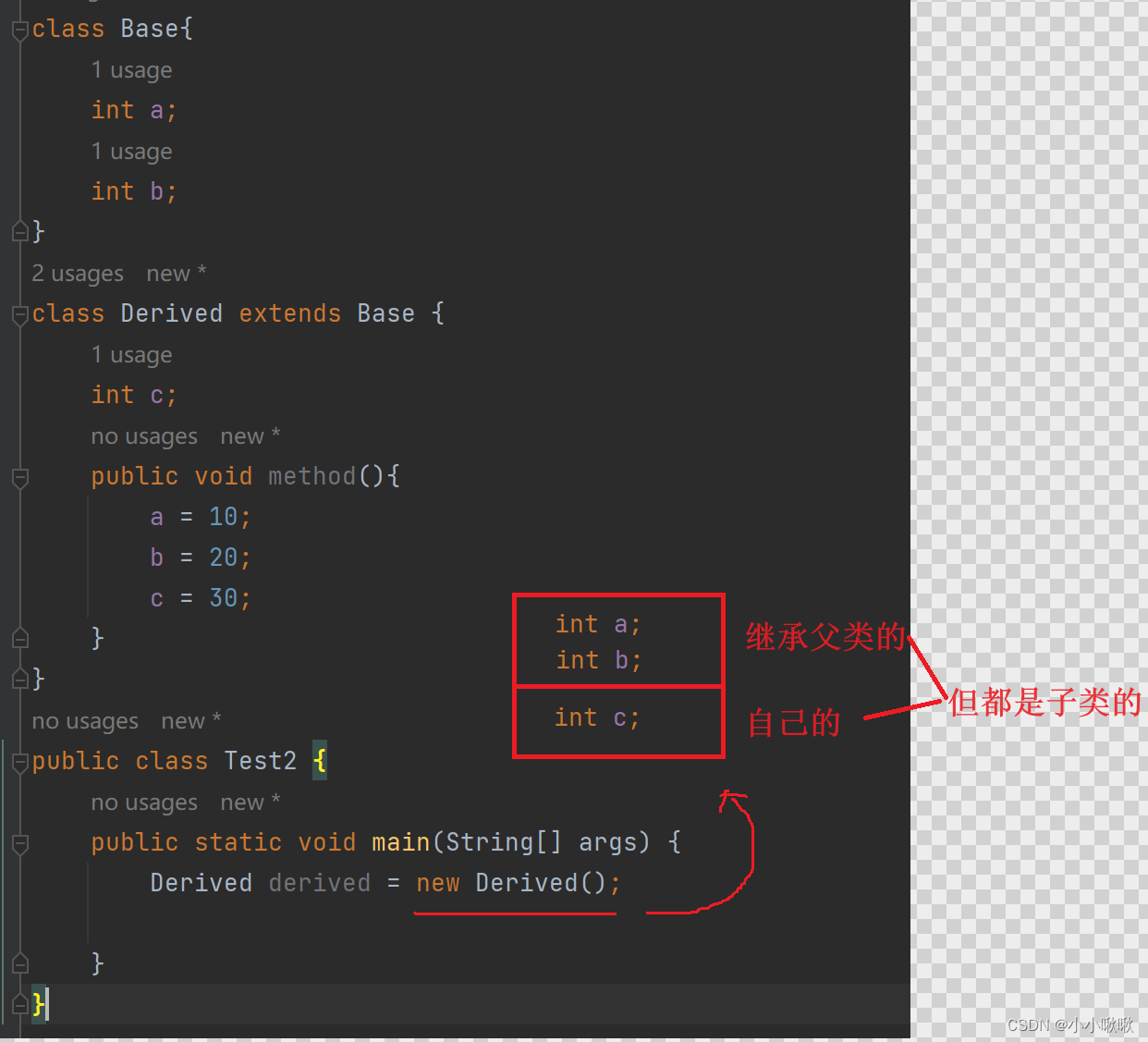
class Base{public int a = 15;public int b = 20;
}
class Derived extends Base {public int a = 77;public void method(){System.out.println("a = "+a);System.out.println("b = "+b);}
}
public class Test2 {public static void main(String[] args) {Derived derived = new Derived();derived.method();//输出 a = 77 // b = 20}
}
子类中访问父类的成员方法
1. .子类和父类的成员方法名字不同
class Base{public void method(){System.out.println("Base:method:");}
}
class Derived extends Base{public void method2(){System.out.println("Derived:method:");}public void tset3(){method();method2();}
}
public class Test2 {public static void main(String[] args) {Derived derived = new Derived();derived.tset3();// 输出 Base:method://Derived:method:}
}
2…子类和父类的成员方法名字相同
class Base{public void method(){System.out.println("Base:method:");}
}
class Derived extends Base{public void method2(){System.out.println("Derived:method:");}public void method(){System.out.println("Derived:method:");}public void tset3(){method();method2();}
}
public class Test2 {public static void main(String[] args) {Derived derived = new Derived();derived.tset3();//输出 Derived:method:// Derived:method:}
}
这时候说
public void method(){System.out.println("Derived:method:");
//和public void method(){System.out.println("Base:method:");}//构成重载了
总结:
1.通过子类对象访问父类与子类中不同名方法时,优先在子类中找,找不到去父类找,两者都找不到则编译报错。
2.通过派生类对象访问父类与子类同名方法时,优先访问子类的成员方法
super关键字(在子类中访问父类成员)
如果要在子类方法中访问父类同名成员时,Java提供了super关键字,该关键字主要作用:在子类方法中访问父类的成员
1. 访问父类的成员方法
class Base{public void method(){System.out.println("Base:method:");}
}
class Derived extends Base{public void method2(){System.out.println("Derived:method:");}public void method(){System.out.println("Derived:method:");}public void tset3(){super.method();method2();}
}
public class Test2 {public static void main(String[] args) {Derived derived = new Derived();derived.tset3();//输出 Base:method:// Derived:method:}
}
2.访问父类的成员变量
class Base{public int a = 15;public int b = 20;
}
class Derived extends Base {public int a = 77;public void method(){System.out.println("a = "+super.a);System.out.println("b = "+b);}
}
public class Test2 {public static void main(String[] args) {Derived derived = new Derived();derived.method();}
}
【注意事项】
- 只能在非静态方法中使用
总结:
在子类方法中,如果想要明确访问父类中成员时,借助super关键字即可。
总结
本章内容较容易理解,理解继承的原理,语法是修饰符 class 子类 extends 父类,子类继承父类用extends关键字,在成员名字相同时在子类中访问父类成员用supet关键字。
99%的人还看了
相似问题
猜你感兴趣
版权申明
本文"【继承之extends关键字和super关键字】":http://eshow365.cn/6-25717-0.html 内容来自互联网,请自行判断内容的正确性。如有侵权请联系我们,立即删除!