已解决
C++入门(3):引用,内联函数
来自网友在路上 178878提问 提问时间:2023-10-24 16:15:50阅读次数: 78
最佳答案 问答题库788位专家为你答疑解惑
一、引用
1.1 引用特性
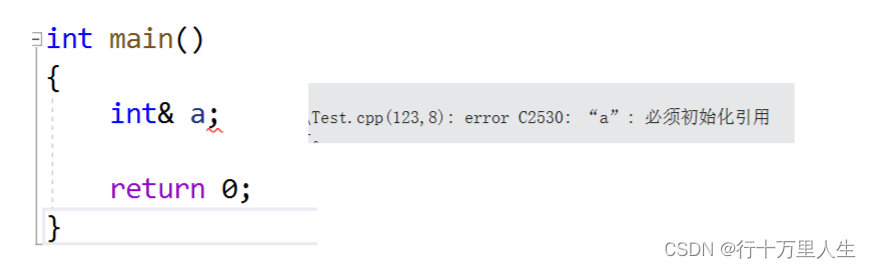
- 引用必须初始化
-
一个变量可以有多个引用
-
引用一旦引用一个实体,就不能引用其他实体
int main()
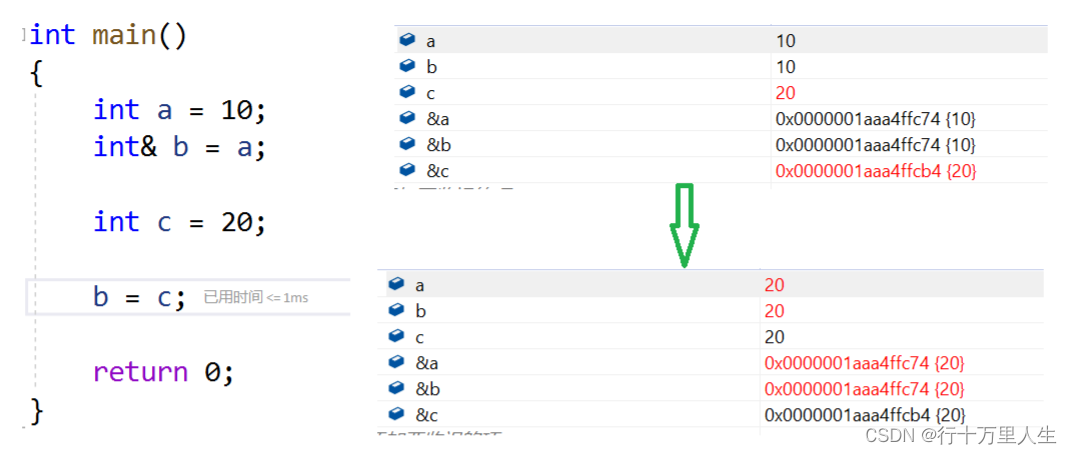
{int a = 10, C = 20;int& b = a;b = c; // 赋值?还是b变成c的别名?return 0;
}
1.2 常引用
引用权限可以平移或缩小,但是不能放大。
int main()
{// 情形1const int a = 10;// int& a1 = a; // errorconst int& a2 = a;// 情形2// int& b = 10; // errorconst int& b1 = 10;// 10具有常属性,权限平移// 情形3int c = 10;// double& c1 = c;// error,类型不同const double& c2 = c;// 隐式类型转换过程中,会创建一个具有常属性的临时变量return 0;
}
1.3 使用场景
- 做参数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;void Swap(int& x, int& y)
{int tmp = x;x = y;y = x;
}int main()
{int a = 10;int b = 20;Swap(a, b);return 0;
}
- 做返回值
观察以下几个场景。
(a).
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int count1()
{int n = 0;n++;return n;
}int& count2()// 实际上是个错误程序
{int n = 0;n++;return n;
}int& count3()
{static int n = 0;n++;return n;
}int main()
{int ret1 = count1();cout << ret1 << endl;int ret2 = count2();cout << ret2 << endl;int& ret3 = count2();// ret3是n的别名,count2函数栈帧销毁后,ret3/n 的值是不确定的cout << ret3 << endl;cout << ret3 << endl;int& ret4 = count3();cout << ret4 << endl;return 0;
}
(b).
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;// static
int& Add1(int a, int b)
{static int c = a + b;return c;
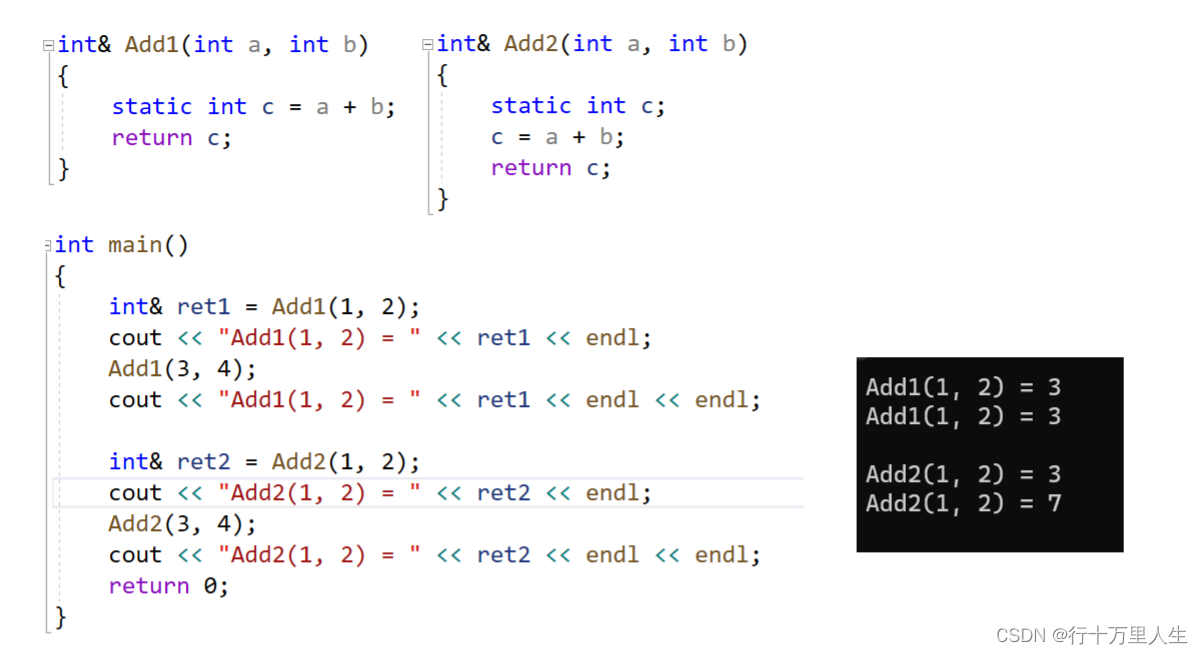
}int& Add2(int a, int b)
{static int c;c = a + b;return c;
}int main()
{int& ret1 = Add1(1, 2);cout << "Add1(1, 2) = " << ret1 << endl;Add1(3, 4);cout << "Add1(1, 2) = " << ret1 << endl << endl;int& ret2 = Add2(1, 2);cout << "Add2(1, 2) = " << ret2 << endl;Add2(3, 4);cout << "Add2(1, 2) = " << ret2 << endl << endl;return 0;
}
1.4 传值、传引用效率比较
以值作为参数或返回值类型,在传参和返回期间,函数不会传递实参或将变量本身直接返回,而是传递实参或返回变量的一份临时拷贝。因此用值作为参数或返回值类型,效率非常低下。
1.5 引用和指针的区别
在语法概念上,引用是被引用实体变量的别名,并没有开辟新的内存空间。

在底层实现上,实际开了空间。引用是按照指针的方式实现的。

二、内联函数
2.1 概念
内联函数是用关键词 inline 修饰的函数,可以代替宏函数(宏函数缺点:1. 语法细节多,易出错;2. 不可调试;3. 没有类型安全检查)。
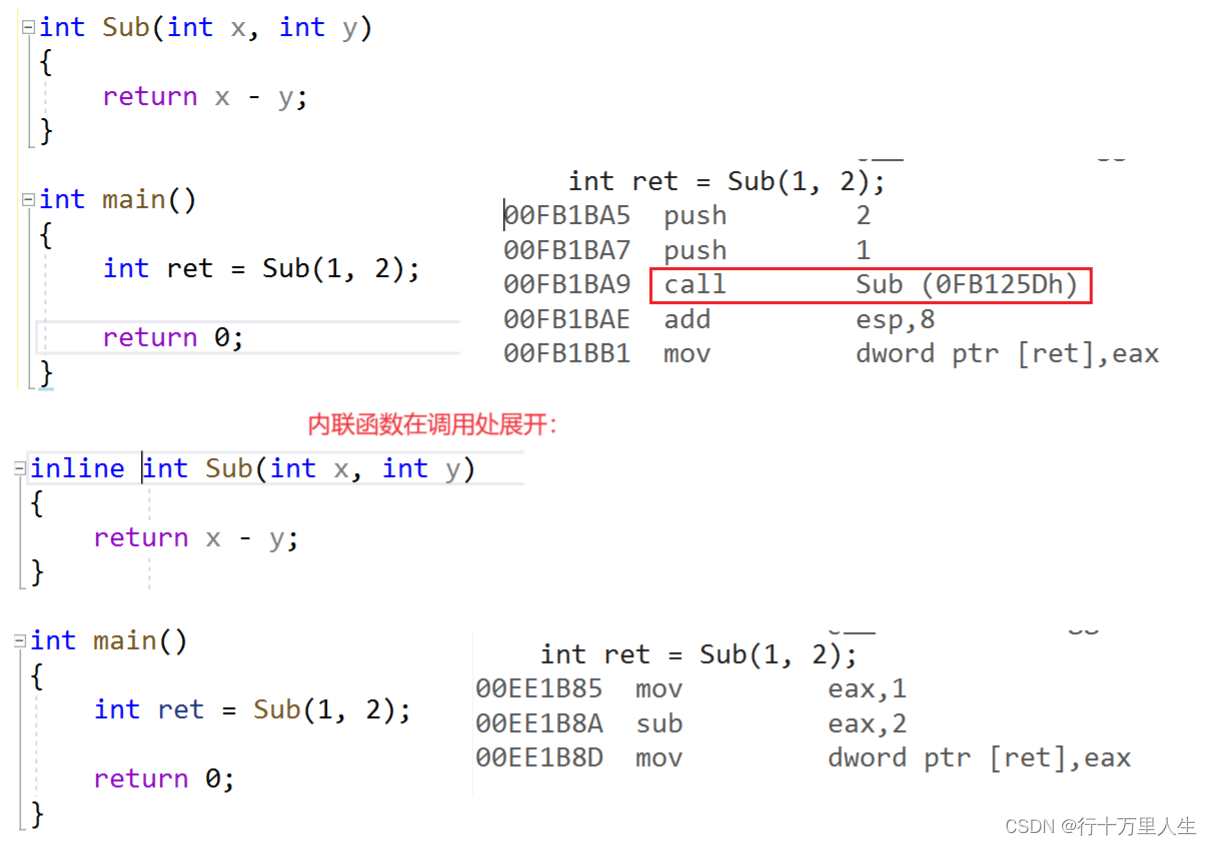
编译时,C++编译器会在把内联函数在调用位置展开,没有建立函数栈帧的开销,在一定程度上提高程序运行效率。
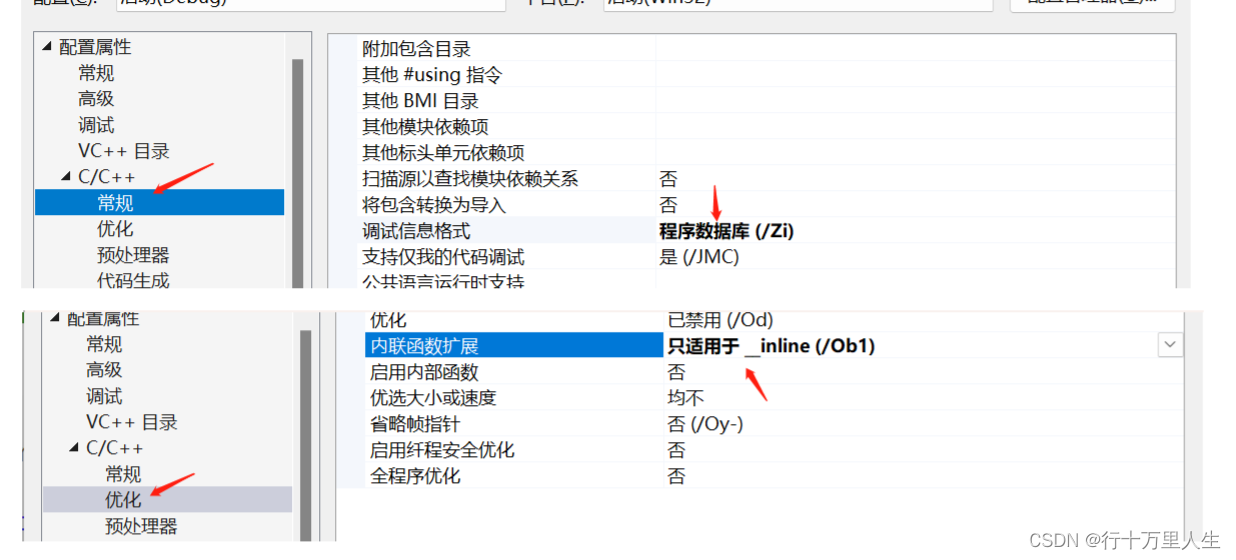
(在debug模式下,编译器默认不会对代码进行优化,需要通过设置以观察到内联函数)
右击项目,进入 属性
2.2 特性
- inline 是一种以空间换时间的做法,在编译阶段,会用函数体替换函数调用。
- inline 对编译器来说只是一个“请求”,编译器可以选择忽略。一般建议:将函数规模较小、不是递归、频繁调用的函数用 inline 修饰,否则编译器会忽略 inline 特性。
- inline 不能声明和定义分离,分离会导致链接错误——inline 被展开就没有函数地址了。
// Func.h
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;inline void f(int x);// Func.cpp
#include "Func.h"void f(int x)
{cout << "f(x)" << endl;
}// test.cpp
#include "Func.h"int main()
{f(10);return 0;
}// error:
// 链接错误:Test.obj : error LNK2019: 无法解析的外部符号 "void __cdecl f(int)" (?f@@YAXH@Z),函数 _main 中引用了该符号
正确做法:
// Func.h #include <iostream> using namespace std;inline void f(int x) {cout << "f(x)" << endl; }
查看全文
99%的人还看了
相似问题
猜你感兴趣
版权申明
本文"C++入门(3):引用,内联函数":http://eshow365.cn/6-23479-0.html 内容来自互联网,请自行判断内容的正确性。如有侵权请联系我们,立即删除!
- 上一篇: Snowflake雪花算法
- 下一篇: [尚硅谷React笔记]——第5章 React 路由