C++笔记之popen()和std_system()和std_async()执行系统命令比较
最佳答案 问答题库638位专家为你答疑解惑
C++笔记之popen()和std_system()和std_async()执行系统命令比较
code review!
文章目录
- C++笔记之popen()和std_system()和std_async()执行系统命令比较
- 1.popen()
- 2.std::system()
- 3.std::async()——C++11提供的异步操作库,适合在多线程中执行外部命令,建议使用!
- std::async和std::future
- 4.system()和std::async结合使用
- 5.popen()和std::async结合使用
1.popen()
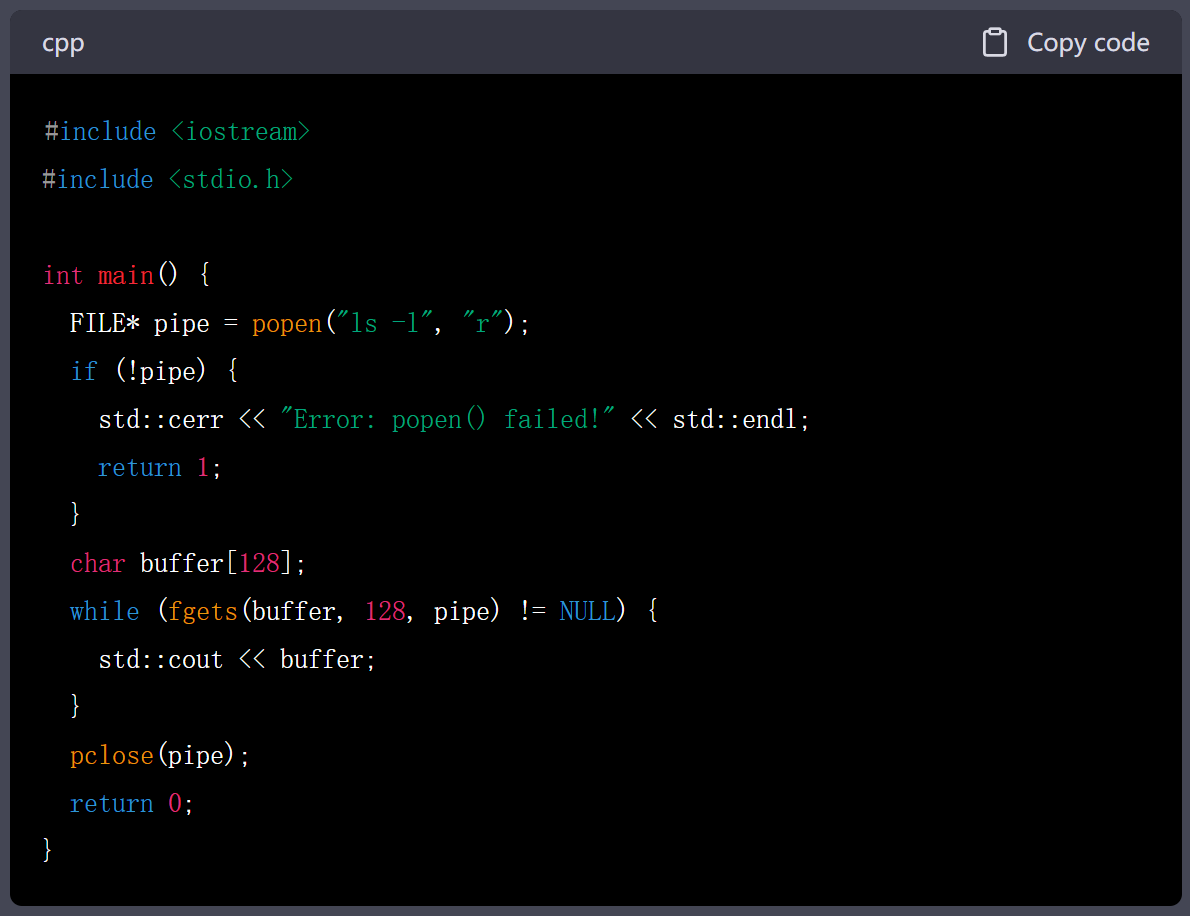
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE* pipe = popen("ls -l", "r");if (!pipe) {std::cerr << "Error: popen() failed!" << std::endl;return 1;}char buffer[128];while (fgets(buffer, 128, pipe) != NULL) {std::cout << buffer;}pclose(pipe);return 0;
}
2.std::system()
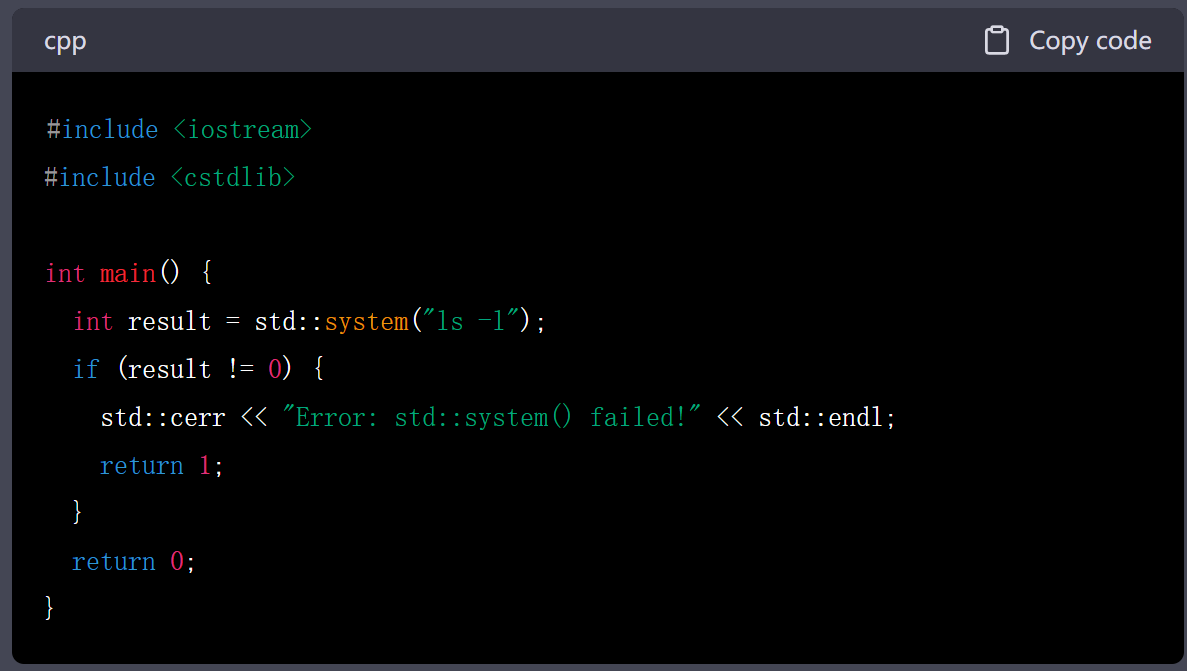
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>int main() {int result = std::system("ls -l");if (result != 0) {std::cerr << "Error: std::system() failed!" << std::endl;return 1;}return 0;
}

3.std::async()——C++11提供的异步操作库,适合在多线程中执行外部命令,建议使用!

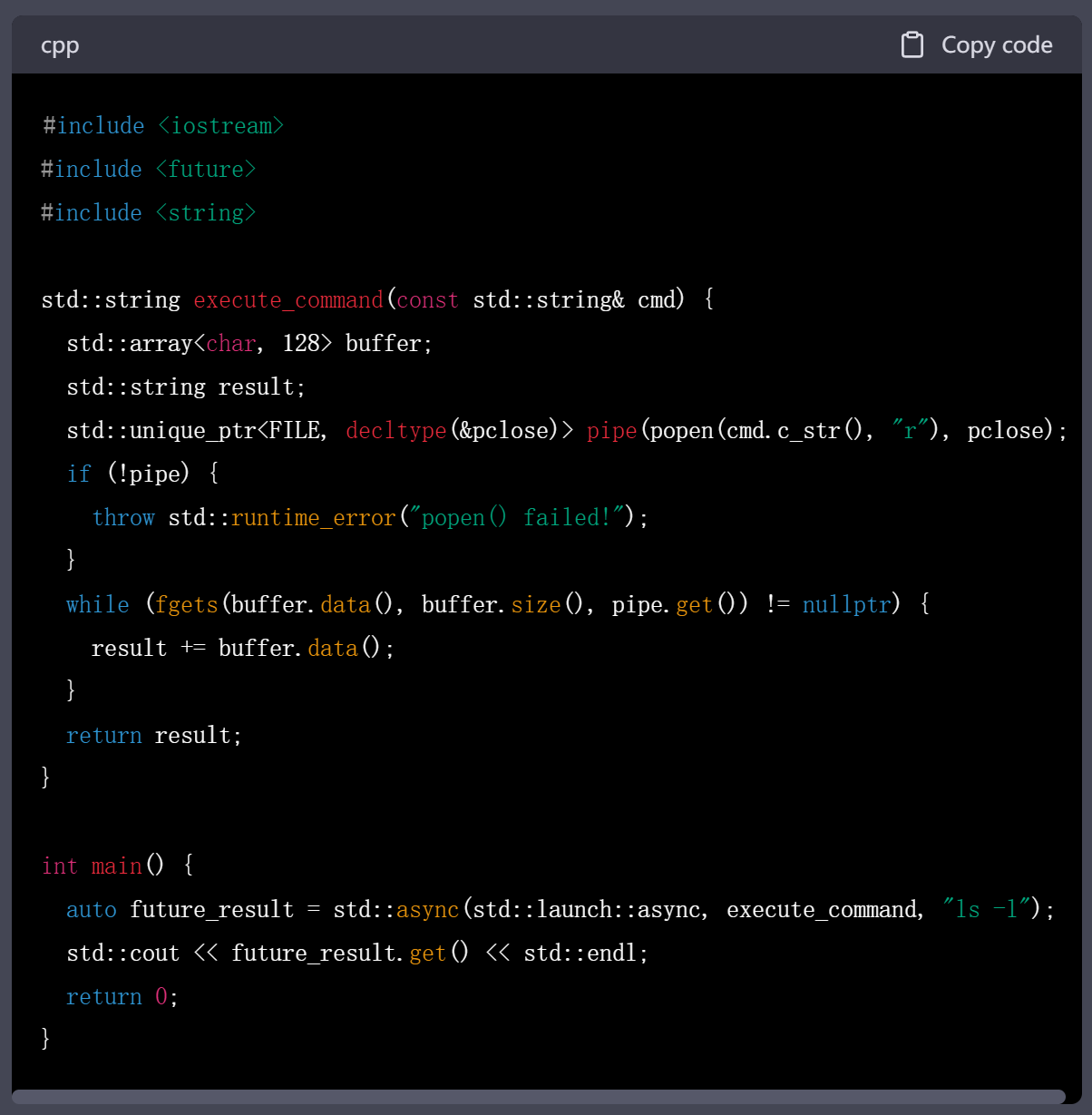
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <future>
#include <string>std::string execute_command(const std::string& cmd) {std::array<char, 128> buffer;std::string result;std::unique_ptr<FILE, decltype(&pclose)> pipe(popen(cmd.c_str(), "r"), pclose);if (!pipe) {throw std::runtime_error("popen() failed!");}while (fgets(buffer.data(), buffer.size(), pipe.get()) != nullptr) {result += buffer.data();}return result;
}int main() {auto future_result = std::async(std::launch::async, execute_command, "ls -l");std::cout << future_result.get() << std::endl;return 0;
}
上面的代码会在新的线程中异步执行"ls -l"命令,并将输出结果存储在一个字符串中。通过std::async和std::future的组合,可以轻松地在多线程环境中执行外部命令,避免了阻塞主线程的问题。
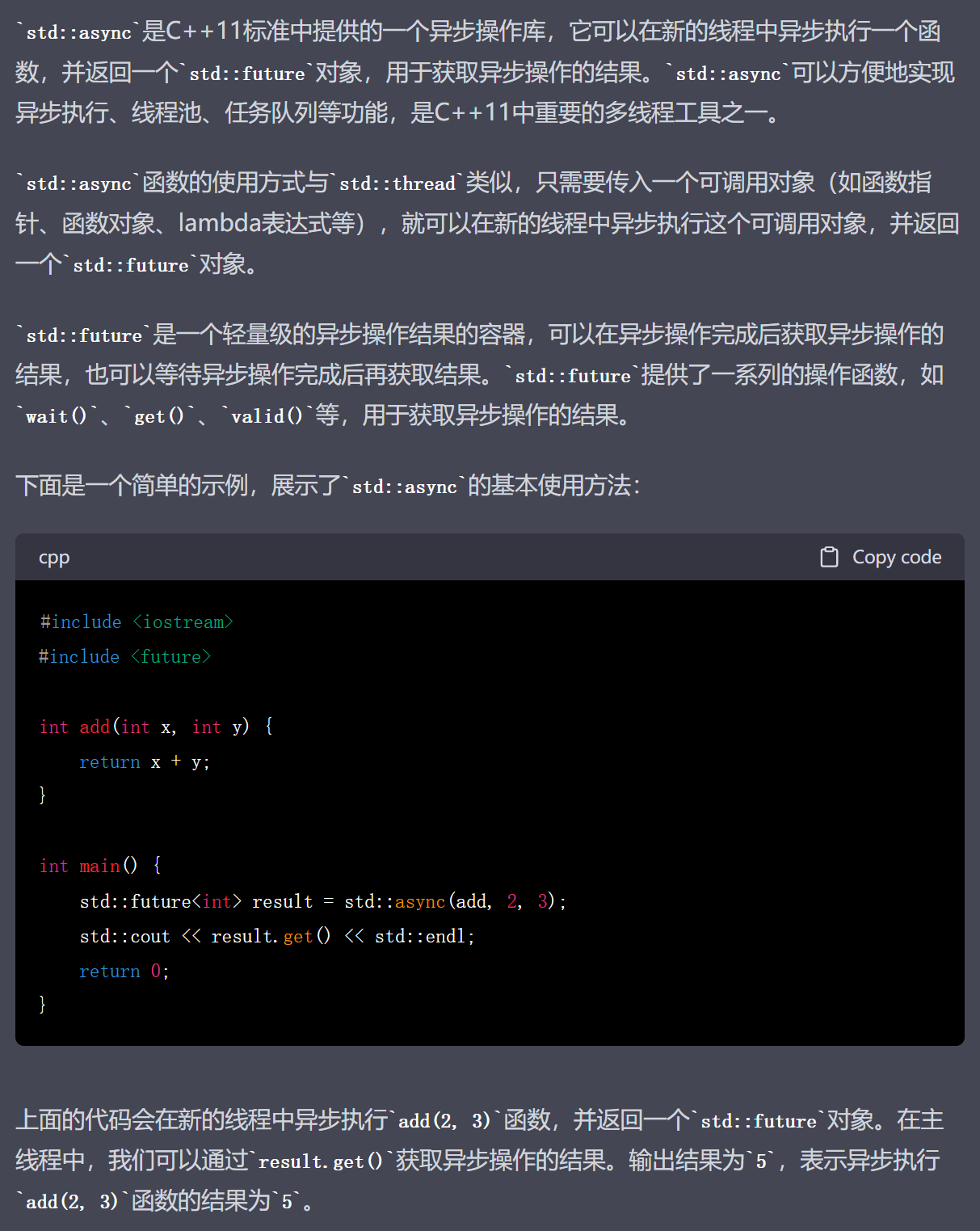
std::async和std::future
4.system()和std::async结合使用
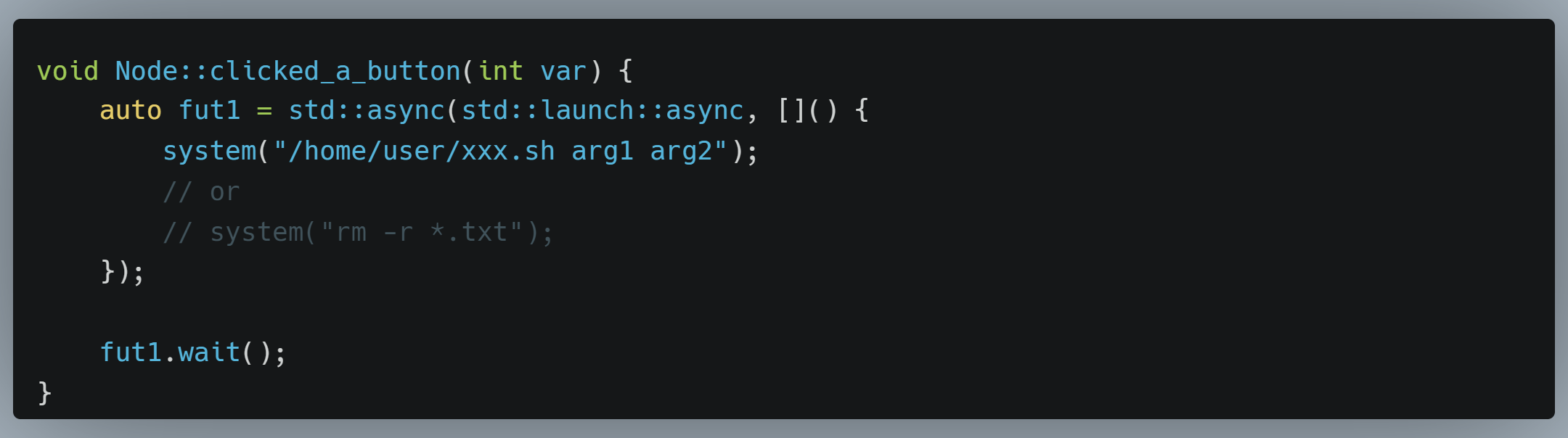
void Node::clicked_a_button(int var) {auto fut1 = std::async(std::launch::async, []() {system("/home/user/xxx.sh arg1 arg2");// or// system("rm -r *.txt");});fut1.wait();
}
这段代码是一个C++函数,涉及到多线程编程和系统调用。让我们逐行分析:
-
void Node::clicked_a_button(int var)是一个成员函数,可能属于一个类(Node),接受一个整数参数var。 -
auto fut1 = std::async(std::launch::async, []() { ... });创建了一个异步任务(使用std::async)并将其分配给名为fut1的std::future对象。这个异步任务使用std::launch::async策略,表示它应该在一个新的线程中异步执行。 -
system("/home/user/xxx.sh arg1 arg2");这是一个系统调用,用于执行外部的shell脚本(xxx.sh)并传递两个参数(arg1和arg2)。这个命令将在一个新的子进程中运行,通常用于执行外部命令。 -
fut1.wait();这一行等待异步任务(在fut1中)的完成。这会导致主线程阻塞,直到异步任务执行完毕。
需要注意的是,虽然std::async用于启动异步任务,但在此代码中,主线程仍然会等待异步任务完成,因为在 fut1.wait(); 处进行了显式等待。这意味着异步任务的效果仅在执行系统调用期间是异步的,而在 fut1.wait(); 处,主线程将被阻塞,直到系统调用完成。
这种用法可以用于在C++中启动外部进程或shell脚本,但需要小心,因为system函数在执行时会阻塞主线程,可能导致整个应用程序在执行外部命令时暂停。如果需要更多的并发性,可以考虑使用std::thread或其他多线程库来在后台执行系统调用,以便主线程可以继续执行其他任务。
5.popen()和std::async结合使用
- 1.执行外部shell脚本并传递参数的简单例程
在C++中,您可以使用popen函数来执行外部Shell脚本,并使用std::async来异步执行它。下面是一个简单的例程,演示如何结合使用这两个功能来执行外部Shell脚本并传递参数。
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <future>
#include <string>int executeShellScript(const std::string& scriptPath, const std::string& argument) {std::string command = scriptPath + " " + argument;FILE* pipe = popen(command.c_str(), "r");if (!pipe) {std::cerr << "Error executing the shell script." << std::endl;return -1;}char buffer[128];std::string result = "";while (!feof(pipe)) {if (fgets(buffer, 128, pipe) != nullptr) {result += buffer;}}int exitCode = pclose(pipe);if (exitCode == -1) {std::cerr << "Error closing the pipe." << std::endl;return -1;}std::cout << "Shell script output: " << result;return exitCode;
}int main() {std::string scriptPath = "your_script.sh";std::string argument = "your_argument";std::future<int> result = std::async(std::launch::async, executeShellScript, scriptPath, argument);// You can perform other tasks while the script is running asynchronouslyint exitCode = result.get();std::cout << "Shell script exited with code: " << exitCode << std::endl;return 0;
}
在上面的示例中,executeShellScript 函数接受Shell脚本的路径和要传递给脚本的参数。它使用 popen 执行脚本,并在异步任务中调用它。在 main 函数中,std::async 用于启动异步任务执行外部脚本。您可以在启动异步任务后执行其他任务,然后使用 result.get() 来等待异步任务的完成并获取返回的退出码。
请替换 "your_script.sh" 和 "your_argument" 为实际的脚本路径和参数。确保您的脚本在执行时可以接受参数并处理它们。
- 2.执行linux系统命令的简单例程
在C++中,您可以结合使用popen函数和std::async来执行Linux系统命令。下面是一个简单的例程,演示如何执行Linux系统命令并获取其输出。
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <future>
#include <string>std::string executeLinuxCommand(const std::string& command) {FILE* pipe = popen(command.c_str(), "r");if (!pipe) {std::cerr << "Error executing the command." << std::endl;return "";}char buffer[128];std::string result = "";while (!feof(pipe)) {if (fgets(buffer, 128, pipe) != nullptr) {result += buffer;}}int status = pclose(pipe);if (status == -1) {std::cerr << "Error closing the pipe." << std::endl;return "";}return result;
}int main() {std::string command = "ls -l"; // Replace with the desired Linux commandstd::future<std::string> result = std::async(std::launch::async, executeLinuxCommand, command);// You can perform other tasks while the command is running asynchronouslystd::string commandOutput = result.get();std::cout << "Command output:\n" << commandOutput;return 0;
}
在上面的示例中,executeLinuxCommand 函数接受要执行的Linux命令,并使用 popen 执行该命令。然后,通过 std::async 在异步任务中调用它。在 main 函数中,std::async 用于启动异步任务执行Linux命令。您可以在启动异步任务后执行其他任务,然后使用 result.get() 来等待异步任务的完成并获取命令的输出。
请替换"ls -l"为您要执行的实际Linux命令。这个示例只是一个演示,您可以根据需要替换命令。确保您的Linux命令能够在Shell中正常执行。
99%的人还看了
相似问题
猜你感兴趣
版权申明
本文"C++笔记之popen()和std_system()和std_async()执行系统命令比较":http://eshow365.cn/6-19445-0.html 内容来自互联网,请自行判断内容的正确性。如有侵权请联系我们,立即删除!
- 上一篇: kafka属性说明
- 下一篇: QMidi Pro for Mac:打造您的专属卡拉OK体验