Linux 内存workingset Refault Distance算法源码及源码解析
最佳答案 问答题库518位专家为你答疑解惑
概述
内核mm子系统中有一个workingset.c实现了refault distance算法,发现网络逻辑介绍该算法的文章主要是复制自奔跑吧内核一书中的内容,均比较雷同,讲述的角度比较难以理解,我第一看到的时候琢磨了2天才明白,本文希望从更容易理解的角度来分析何为refault distance算法,以及内核引入该算法的原因,这就要从内核回收page面临的挑战说起。本文源码:v5.9
page回收的问题
以read/write读取文件场景来举例,我们知道内核会生成page cache加速读写过程,而这些缓存有可能是一次性的,也有可能是不断重复使用,具体要看应用程序的代码时怎么实现的,所以内核很难预测页面的使用趋势,毕竟内核也不能未卜先知,在这个前提下,那么这种page cache新创建的时候到底是加入active lru还是inactive lru呢?内核引入workingset refault distance算法后,新一点内核(比如5.9及以后)都将page先加入inactive lru列表中,因为贸然加入active lru中,大量的page产生之后,就很容易把真正hot的page挤到inactive lru当中,这个很明显是不合理。
那么放入Inactive lru链表中岂不是很容易回收误伤?
没有workingset refault distance算法签确实如此,所以低版本内核对于anon page新产生时加入的是active lru列表。但是引入refault distance算法后,如上所述都是加入inactive lru列表中,如果page被内存回收,而应用程序再次访问,触发的缺页叫:refault。那么问题来了,refault之后这个page到底是放入active lru还是inactive lru呢?
要想解决这个问题我们要看下加入active lru和inactive lru的利弊:
- 放入inactive lru:这个page相对更容易被回收掉,可能造成性能损失。
- 放入active lru,相对更不容回收,如果这个page后续访问频率依然很高,这样很有利,但是如果page后续不再访问,放入active就亏了。还有一种情况是,如果后续继续访问,但是访问的间隔很长,放入active lru也是没用的....
所以上面到底决定是加入哪个lru链表,本质上是无法“精准”预测的,只能根据已经的使用情况来评估此次refault到底是将page放入哪个lru链表,那么怎么实现呢,这就是“refault distance"算法要做的。
我们知道知道放入active比inactive更不容回收,原因是因为内核的LRU算法的老化方法决定,inactive被回收之后,发现active:inactive比例失调,inactive链表的page比较多时候,就会将active lru中的page move到inactive链表中,所以如果放入active lru当中,page抵抗更久的内存回收。
假设page被回收的时候(eviction)的系统回收page的数量是E,再次读取refault时候系统回收的page的数量增加到了R,那么这段时间系统回收page的数量是:R - E,这个称为算法的refault distance,再假设active lru中page数量为:num(active_lru),我们来想象一下,如果R - E的数量小于num(active_lru) ,那么refault将page加入active lru的话,如果page后续还是保持当前的access interval,那么就可以避免再次被回收后refault导致的性能颠簸。如果num(active_lru) < R - E,那么加入active lru也没有用,因为访问间隔太长了,即使放入active lru也无法避免被回收(假设还是保持当前的access interval):

源码解析
内核源码实现上述算法的时候要有如下几个要点(参考上图)
- T1时候页面被回收剔除LRU,系统要把当前系统被回收的页面数量记录下来假设E(比如100),内核是记录到radix tree当中(以file-back page举例),并且标识成一个”value",这样跟正常情况保存page pointer做区分。内核通过workingset_eviction函数实现该过程。
- T2时候重新读取该page的时候,发现radix tree中是个特殊的“value",就将其保存的T1时候的回收页面数量E读取出来为100,T2时候回收页面数量R,假设是200,说明这个期间系统回收了100个页面,假设active lru页面超过100,那么refault时候把page加入active,否则放入inactive lru。内核通过workingset_refault实现该过程中。
workingset_eviction
调用路径:shrink_page_list--->workingset_eviction
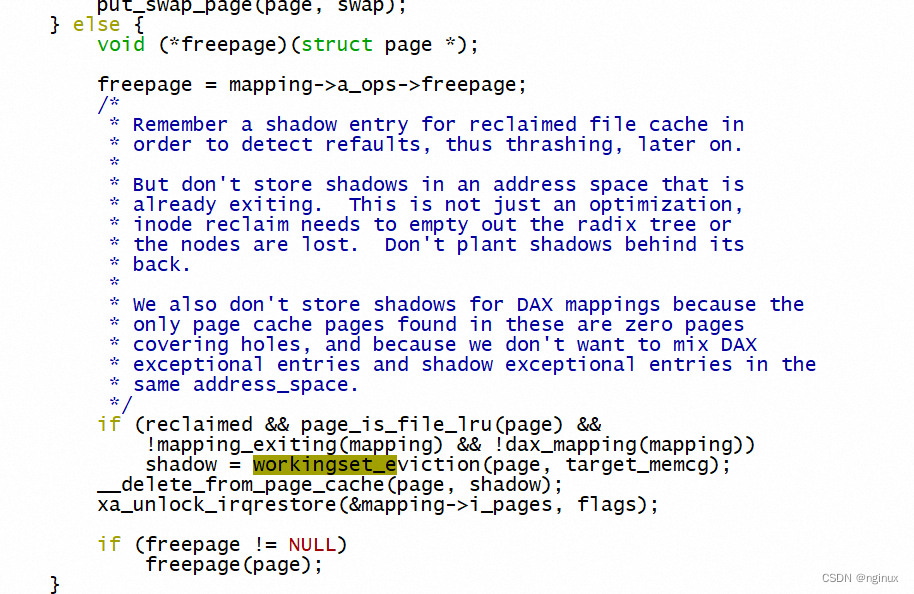
shrink_page_list成功回收页面的时候,将page从LRU和page cache中删除,就会调用workingset_eviction:
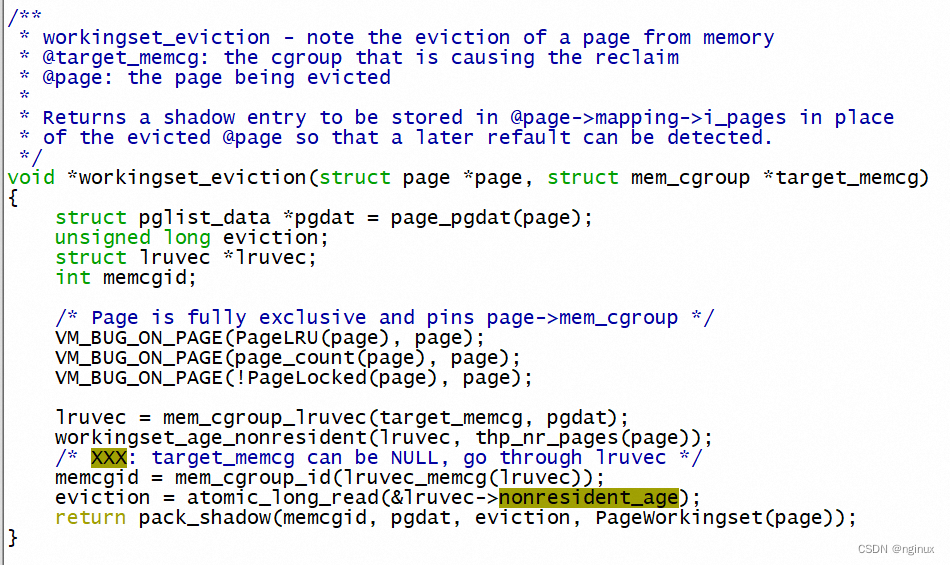
可以看到workingset_eviction读取出来lruvec->nonresident_age(对应上面提到的E 100这个之),然后pack_shadow编码之后存储到radix tree当中,由于这个时候page已经从page cache的radix tree删除,所以这种一个叫做”value"的exception entry,这个可以从pack_shadow源码看到:

workingset_refault
下面是workingset_refault的源码
/*** workingset_refault - evaluate the refault of a previously evicted page* @page: the freshly allocated replacement page* @shadow: shadow entry of the evicted page** Calculates and evaluates the refault distance of the previously* evicted page in the context of the node and the memcg whose memory* pressure caused the eviction.*/
void workingset_refault(struct page *page, void *shadow)
{bool file = page_is_file_lru(page);struct mem_cgroup *eviction_memcg;struct lruvec *eviction_lruvec;unsigned long refault_distance;unsigned long workingset_size;struct pglist_data *pgdat;struct mem_cgroup *memcg;unsigned long eviction;struct lruvec *lruvec;unsigned long refault;bool workingset;int memcgid;unpack_shadow(shadow, &memcgid, &pgdat, &eviction, &workingset);rcu_read_lock();/** Look up the memcg associated with the stored ID. It might* have been deleted since the page's eviction.** Note that in rare events the ID could have been recycled* for a new cgroup that refaults a shared page. This is* impossible to tell from the available data. However, this* should be a rare and limited disturbance, and activations* are always speculative anyway. Ultimately, it's the aging* algorithm's job to shake out the minimum access frequency* for the active cache.** XXX: On !CONFIG_MEMCG, this will always return NULL; it* would be better if the root_mem_cgroup existed in all* configurations instead.*/eviction_memcg = mem_cgroup_from_id(memcgid);if (!mem_cgroup_disabled() && !eviction_memcg)goto out;eviction_lruvec = mem_cgroup_lruvec(eviction_memcg, pgdat);refault = atomic_long_read(&eviction_lruvec->nonresident_age);/** Calculate the refault distance** The unsigned subtraction here gives an accurate distance* across nonresident_age overflows in most cases. There is a* special case: usually, shadow entries have a short lifetime* and are either refaulted or reclaimed along with the inode* before they get too old. But it is not impossible for the* nonresident_age to lap a shadow entry in the field, which* can then result in a false small refault distance, leading* to a false activation should this old entry actually* refault again. However, earlier kernels used to deactivate* unconditionally with *every* reclaim invocation for the* longest time, so the occasional inappropriate activation* leading to pressure on the active list is not a problem.*/refault_distance = (refault - eviction) & EVICTION_MASK;/** The activation decision for this page is made at the level* where the eviction occurred, as that is where the LRU order* during page reclaim is being determined.** However, the cgroup that will own the page is the one that* is actually experiencing the refault event.*/memcg = page_memcg(page);lruvec = mem_cgroup_lruvec(memcg, pgdat);inc_lruvec_state(lruvec, WORKINGSET_REFAULT_BASE + file);/** Compare the distance to the existing workingset size. We* don't activate pages that couldn't stay resident even if* all the memory was available to the workingset. Whether* workingset competition needs to consider anon or not depends* on having swap.*/workingset_size = lruvec_page_state(eviction_lruvec, NR_ACTIVE_FILE);if (!file) {workingset_size += lruvec_page_state(eviction_lruvec,NR_INACTIVE_FILE);}if (mem_cgroup_get_nr_swap_pages(memcg) > 0) {workingset_size += lruvec_page_state(eviction_lruvec,NR_ACTIVE_ANON);if (file) {workingset_size += lruvec_page_state(eviction_lruvec,NR_INACTIVE_ANON);}}if (refault_distance > workingset_size)goto out;SetPageActive(page);workingset_age_nonresident(lruvec, thp_nr_pages(page));inc_lruvec_state(lruvec, WORKINGSET_ACTIVATE_BASE + file);/* Page was active prior to eviction */if (workingset) {SetPageWorkingset(page);/* XXX: Move to lru_cache_add() when it supports new vs putback */spin_lock_irq(&page_pgdat(page)->lru_lock);lru_note_cost_page(page);spin_unlock_irq(&page_pgdat(page)->lru_lock);inc_lruvec_state(lruvec, WORKINGSET_RESTORE_BASE + file);}
out:rcu_read_unlock();
}- unpack_shadow:读出来E只(举例中的100值)
- refault = atomic_long_read(&eviction_lruvec->nonresident_age); 读取refault时候的系统nonresident_age数量,对应上面例子中的R = 200.
- refault_distance = 200 - 100 = 100
- workingset_size 保存active lru的page数量
- if (refault_distance > workingset_size)直接goto out,因为即使加入active lru也没法保护page;否则setPageActive,说明实要放入active lru当中的。
99%的人还看了
相似问题
猜你感兴趣
版权申明
本文"Linux 内存workingset Refault Distance算法源码及源码解析":http://eshow365.cn/6-13208-0.html 内容来自互联网,请自行判断内容的正确性。如有侵权请联系我们,立即删除!