WebGL 选中一个表面
最佳答案 问答题库878位专家为你答疑解惑
目录
选中一个表面
示例程序(PickFace.js)
代码详解
示例效果
选中一个表面
WebGL 选中物体_山楂树の的博客-CSDN博客可以使用同样的方法来选中物体的某一个表面。这一节在PickObject程序的基础上编写了PickFace程序,后者同样包含一个立方体,但用户可以选中立方体的某一个表面,被选中的表面会变成白色。下图显示了PickFace的运行效果。
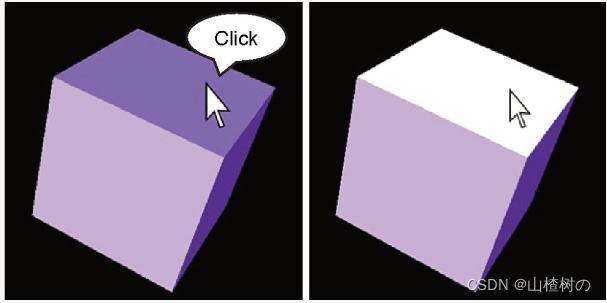
如果你理解了PickObject的程序原理,那么PickFace就很简单了。PickObject用户在点击鼠标时,将立方体重绘为红色,然后读取鼠标点击位置的像素颜色,根据其是红色或是黑色来判断点击时鼠标是否在立方体上,即是否选中了立方体。而PickFace则更进一步,在用户点击鼠标时重绘立方体,并将“每个像素属于哪个面”的信息写入到颜色缓冲区的α分量中。下面来看一下示例程序。
示例程序(PickFace.js)
PickFace.js的代码如下所示。为了简洁,略去了与前例相同的部分,如顶点着色器等。
// PickFace.js (c) 2012 matsuda and kanda
// Vertex shader program
var VSHADER_SOURCE ='attribute vec4 a_Position;\n' +'attribute vec4 a_Color;\n' +'attribute float a_Face;\n' + // Surface number (Cannot use int for attribute variable)'uniform mat4 u_MvpMatrix;\n' +'uniform int u_PickedFace;\n' + // Surface number of selected face'varying vec4 v_Color;\n' +'void main() {\n' +' gl_Position = u_MvpMatrix * a_Position;\n' +' int face = int(a_Face);\n' + // Convert to int' vec3 color = (face == u_PickedFace) ? vec3(1.0) : a_Color.rgb;\n' +' if(u_PickedFace == 0) {\n' + // In case of 0, insert the face number into alpha' v_Color = vec4(color, a_Face/255.0);\n' +' } else {\n' +' v_Color = vec4(color, a_Color.a);\n' +' }\n' +'}\n';// Fragment shader program
var FSHADER_SOURCE ='#ifdef GL_ES\n' +'precision mediump float;\n' +'#endif\n' +'varying vec4 v_Color;\n' +'void main() {\n' +' gl_FragColor = v_Color;\n' +'}\n';var ANGLE_STEP = 20.0; // Rotation angle (degrees/second)function main() {// Retrieve <canvas> elementvar canvas = document.getElementById('webgl');// Get the rendering context for WebGLvar gl = getWebGLContext(canvas);if (!gl) {console.log('Failed to get the rendering context for WebGL');return;}// Initialize shadersif (!initShaders(gl, VSHADER_SOURCE, FSHADER_SOURCE)) {console.log('Failed to intialize shaders.');return;}// Set the vertex informationvar n = initVertexBuffers(gl);if (n < 0) {console.log('Failed to set the vertex information');return;}// Set the clear color and enable the depth testgl.clearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);gl.enable(gl.DEPTH_TEST);// Get the storage locations of uniform variablesvar u_MvpMatrix = gl.getUniformLocation(gl.program, 'u_MvpMatrix');var u_PickedFace = gl.getUniformLocation(gl.program, 'u_PickedFace');if (!u_MvpMatrix || !u_PickedFace) { console.log('Failed to get the storage location of uniform variable');return;}// Calculate the view projection matrixvar viewProjMatrix = new Matrix4();viewProjMatrix.setPerspective(30.0, canvas.width / canvas.height, 1.0, 100.0);viewProjMatrix.lookAt(0.0, 0.0, 7.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0);// Initialize selected surfacegl.uniform1i(u_PickedFace, -1);var currentAngle = 0.0; // Current rotation angle// Register the event handlercanvas.onmousedown = function(ev) { // Mouse is pressedvar x = ev.clientX, y = ev.clientY;var rect = ev.target.getBoundingClientRect();if (rect.left <= x && x < rect.right && rect.top <= y && y < rect.bottom) {// If Clicked position is inside the <canvas>, update the selected surfacevar x_in_canvas = x - rect.left, y_in_canvas = rect.bottom - y;var face = checkFace(gl, n, x_in_canvas, y_in_canvas, currentAngle, u_PickedFace, viewProjMatrix, u_MvpMatrix);gl.uniform1i(u_PickedFace, face); // Pass the surface number to u_PickedFacedraw(gl, n, currentAngle, viewProjMatrix, u_MvpMatrix);}}var tick = function() { // Start drawingcurrentAngle = animate(currentAngle);draw(gl, n, currentAngle, viewProjMatrix, u_MvpMatrix);requestAnimationFrame(tick, canvas);};tick();
}function initVertexBuffers(gl) {// Create a cube// v6----- v5// /| /|// v1------v0|// | | | |// | |v7---|-|v4// |/ |/// v2------v3var vertices = new Float32Array([ // Vertex coordinates1.0, 1.0, 1.0, -1.0, 1.0, 1.0, -1.0,-1.0, 1.0, 1.0,-1.0, 1.0, // v0-v1-v2-v3 front1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0,-1.0, 1.0, 1.0,-1.0,-1.0, 1.0, 1.0,-1.0, // v0-v3-v4-v5 right1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0,-1.0, -1.0, 1.0,-1.0, -1.0, 1.0, 1.0, // v0-v5-v6-v1 up-1.0, 1.0, 1.0, -1.0, 1.0,-1.0, -1.0,-1.0,-1.0, -1.0,-1.0, 1.0, // v1-v6-v7-v2 left-1.0,-1.0,-1.0, 1.0,-1.0,-1.0, 1.0,-1.0, 1.0, -1.0,-1.0, 1.0, // v7-v4-v3-v2 down1.0,-1.0,-1.0, -1.0,-1.0,-1.0, -1.0, 1.0,-1.0, 1.0, 1.0,-1.0 // v4-v7-v6-v5 back]);var colors = new Float32Array([ // Colors0.32, 0.18, 0.56, 0.32, 0.18, 0.56, 0.32, 0.18, 0.56, 0.32, 0.18, 0.56, // v0-v1-v2-v3 front0.5, 0.41, 0.69, 0.5, 0.41, 0.69, 0.5, 0.41, 0.69, 0.5, 0.41, 0.69, // v0-v3-v4-v5 right0.78, 0.69, 0.84, 0.78, 0.69, 0.84, 0.78, 0.69, 0.84, 0.78, 0.69, 0.84, // v0-v5-v6-v1 up0.0, 0.32, 0.61, 0.0, 0.32, 0.61, 0.0, 0.32, 0.61, 0.0, 0.32, 0.61, // v1-v6-v7-v2 left0.27, 0.58, 0.82, 0.27, 0.58, 0.82, 0.27, 0.58, 0.82, 0.27, 0.58, 0.82, // v7-v4-v3-v2 down0.73, 0.82, 0.93, 0.73, 0.82, 0.93, 0.73, 0.82, 0.93, 0.73, 0.82, 0.93, // v4-v7-v6-v5 back]);var faces = new Uint8Array([ // Faces1, 1, 1, 1, // v0-v1-v2-v3 front2, 2, 2, 2, // v0-v3-v4-v5 right3, 3, 3, 3, // v0-v5-v6-v1 up4, 4, 4, 4, // v1-v6-v7-v2 left5, 5, 5, 5, // v7-v4-v3-v2 down6, 6, 6, 6, // v4-v7-v6-v5 back]);var indices = new Uint8Array([ // Indices of the vertices0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3, // front4, 5, 6, 4, 6, 7, // right8, 9,10, 8,10,11, // up12,13,14, 12,14,15, // left16,17,18, 16,18,19, // down20,21,22, 20,22,23 // back]);// Create a buffer objectvar indexBuffer = gl.createBuffer();if (!indexBuffer) {return -1;}// Write vertex information to buffer objectif (!initArrayBuffer(gl, vertices, gl.FLOAT, 3, 'a_Position')) return -1; // Coordinates Informationif (!initArrayBuffer(gl, colors, gl.FLOAT, 3, 'a_Color')) return -1; // Color Informationif (!initArrayBuffer(gl, faces, gl.UNSIGNED_BYTE, 1, 'a_Face')) return -1;// Surface Information// Unbind the buffer objectgl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, null);// Write the indices to the buffer objectgl.bindBuffer(gl.ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, indexBuffer);gl.bufferData(gl.ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, indices, gl.STATIC_DRAW);return indices.length;
}function checkFace(gl, n, x, y, currentAngle, u_PickedFace, viewProjMatrix, u_MvpMatrix) {var pixels = new Uint8Array(4); // Array for storing the pixel valuegl.uniform1i(u_PickedFace, 0); // Draw by writing surface number into alpha valuedraw(gl, n, currentAngle, viewProjMatrix, u_MvpMatrix);// Read the pixel value of the clicked position. pixels[3] is the surface numbergl.readPixels(x, y, 1, 1, gl.RGBA, gl.UNSIGNED_BYTE, pixels);return pixels[3];
}var g_MvpMatrix = new Matrix4(); // Model view projection matrix
function draw(gl, n, currentAngle, viewProjMatrix, u_MvpMatrix) {// Caliculate The model view projection matrix and pass it to u_MvpMatrixg_MvpMatrix.set(viewProjMatrix);g_MvpMatrix.rotate(currentAngle, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0); // Rotate appropriatelyg_MvpMatrix.rotate(currentAngle, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0);g_MvpMatrix.rotate(currentAngle, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);gl.uniformMatrix4fv(u_MvpMatrix, false, g_MvpMatrix.elements);gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | gl.DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); // Clear buffersgl.drawElements(gl.TRIANGLES, n, gl.UNSIGNED_BYTE, 0); // Draw
}var last = Date.now(); // Last time that this function was called
function animate(angle) {var now = Date.now(); // Calculate the elapsed timevar elapsed = now - last;last = now;// Update the current rotation angle (adjusted by the elapsed time)var newAngle = angle + (ANGLE_STEP * elapsed) / 1000.0;return newAngle % 360;
}function initArrayBuffer (gl, data, type, num, attribute) {// Create a buffer objectvar buffer = gl.createBuffer();if (!buffer) {console.log('Failed to create the buffer object');return false;}// Write date into the buffer objectgl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, buffer);gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, data, gl.STATIC_DRAW);// Assign the buffer object to the attribute variablevar a_attribute = gl.getAttribLocation(gl.program, attribute);if (a_attribute < 0) {console.log('Failed to get the storage location of ' + attribute);return false;}gl.vertexAttribPointer(a_attribute, num, type, false, 0, 0);// Enable the assignment to a_attribute variablegl.enableVertexAttribArray(a_attribute);return true;
}
代码详解
首先,顶点着色器中添加了attribute变量a_Face,它表示立方体各表面的编号,即当前顶点属于哪个表面(第6行)。鼠标被点击时,这个值就会被“编码”成颜色值的α分量。initVertexBuffers()函数(第99行)建立了表面编号数组faces,数组中的每个元素对应一个顶点(第127行)。比如,顶点v0-v1-v2-v3定义了1号表面,而顶点v0-v3-v4-v5定义了2号表面,等等。数组faces前4个元素都是1,表示前4个顶点都属于1号表面,以此类推(第128行)。
当某个表面被选中时,就通过u_PickedFace变量来通知顶点着色器这个表面被选中了(第8行)。这样顶点着色器就可以将这个表面绘制成白色,用户就获得了反馈,知道这个表面确实被选中了。
在正常情况下(即不在鼠标被点击的那一刻),顶点着色器会比较当前被选中的表面编号u_PickedFace和当前顶点的表面编号a_Face,如果它们相等,即当前顶点属于被选中的表面,就将color赋为白色,如果不相等,就将其赋为顶点原来的颜色a_Color。此处必须将float类型的a_Face转化为int类型,再与u_PickedFace进行比较,因为attribute变量只能是float类型的。在鼠标点击的那一刻,u_PickedFace被设为0,我们将a_Face的值写入到颜色的α分量中。
main()函数为u_PickedFace指定初始值-1(第75行)。按照faces变量的定义(第127行),立方体各表面中没有哪一个编号是-1,所以一开始没有任何表面被选中,每一个面的颜色都是初始颜色。
鼠标被点击时,u_PickedFace变量变为了0,顶点着色器就在颜色缓冲区中将每个面绘制成非1的α值,并且α的值取决于表面编号。最关键的逻辑发生在鼠标点击事件的响应函数中:在获取了鼠标点击位置后,调用checkFace()函数并传入u_PickedFace变量,也就是着色器中同名变量的存储地址(第85行)。
checkFace()函数的任务是,根据点击位置返回选中表面的编号(第166行)。该函数首先将u_PickedFace变量设为0(第168行),然后立刻调用draw()函数(在颜色缓冲区中,最终没有显示在屏幕上)进行绘制,此时每个表面的α值就取决于表面的编号。然后,从颜色缓冲区获取鼠标点击处的像素值(第171行),通过pixels[3]获取表面编号(即α分量,索引为3)。checkFace()函数返回选中的表面编号,执行流程回到鼠标点击事件响应函数中,用选中的表面编号重新绘制立方体(第86~87行),并在屏幕上显示出来,如前所述。
示例效果
99%的人还看了
相似问题
猜你感兴趣
版权申明
本文"WebGL 选中一个表面":http://eshow365.cn/6-11143-0.html 内容来自互联网,请自行判断内容的正确性。如有侵权请联系我们,立即删除!